Geospatial Data Science for
WRF-SFIRE Simulations
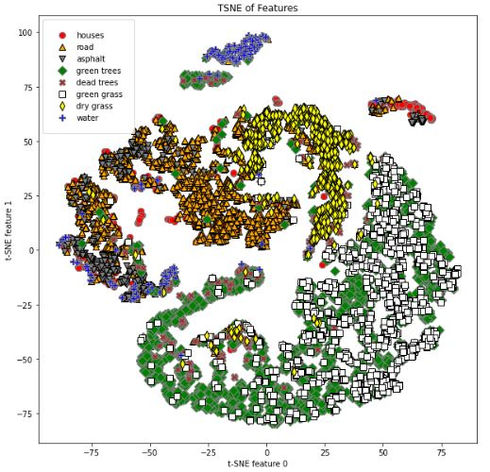
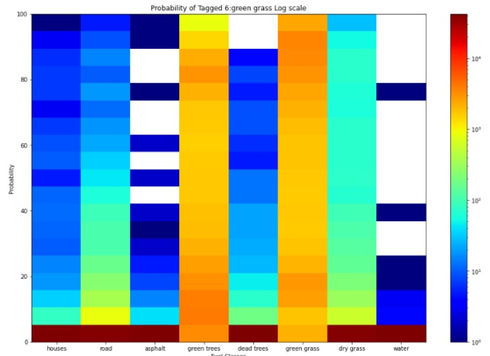
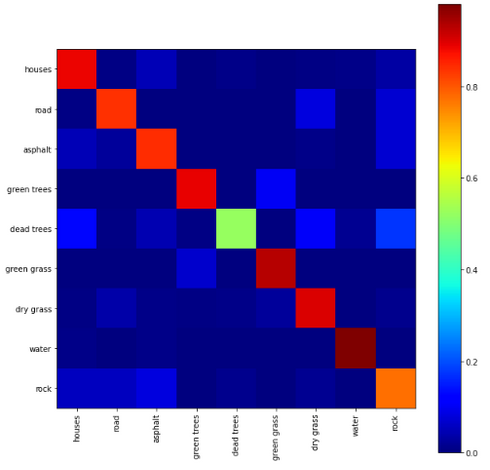
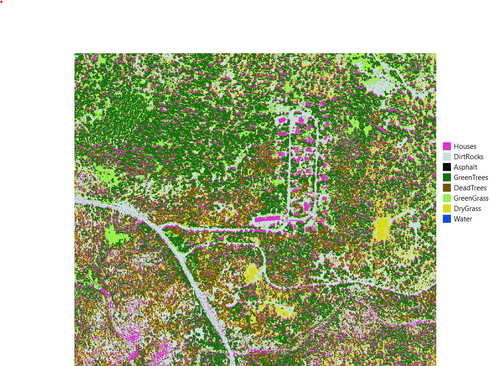
The goal of this project is to create a method of combining machine learning and statistical methods to classify fuel sources of wildfires using 1-meter resolution aerial imagery. The data source was purchased by the Atmospheric Science Group at Lawrence Livermore National Lab from Hexagon Content Program’s Aerial Imagery line. This data covers approximately 280,000 hectares in Sierra National Forest taken on September 3, 2020 right before the California Creek Fire. The data has a spatial resolution of 1-meter with four spectral bands: Red, Green, Blue, and NIR. The outcome so far has been that a combination of a Multi-Layered Perceptron (MLP) Neural Network and the Root Mean Squared Deviation (RMSD) has achieved the highest accuracy at 83.02%. In this initial result, rocks and dirt were placed into the same unburnable class.
Click on the plots below to read more about what they represent!